Lovorka Špirić1, Katarina Huić Babić1, Gert Jan Boelm2
1 Genera Inc., part of Dechra Pharmaceuticals PLC group, Rakov Potok, Croatia
2 Royal GD, Deventer, the Netherlands

Associative use of live attenuated vaccines against avian infectious bronchitis Avishield® IB H120 and Avishield® IB GI-13
Infectious bronchitis(IB)is a highly contagious viral disease of chickens, characterized by damage of respiratory system together with other non respiratory tissues, such as kidneys and reproductive tract. It is ubiquitous in most parts of the world where poultry is reared and it causes severe economic losses by the reduction of weight gain, stunted growth, induction of false layers, and drops in egg production and egg quality. As in the field birds can be exposed to different IB variant strains at the same time, to increase the breadth of protection, flocks are vaccinated with more than one
Aim
The vaccines Avishield IB H120 and Avishield IB GI-13, containing IBV strains H120 and V-173/11 respectively are authorized for use in chickens from 1day of age, however, safety and efficacy of associated use of both vaccines in day old chickens hasn’t been demonstrated so far. The aim of these studies was to evaluate the efficacy of their simultaneous use.
Methods
In three separate studies vaccines were mixed and simultaneously administered to SPF chickens of one day of age in a minimum dose by spray method.
To investigate efficacy against virulent IBV strains, chickens were challenged:
- 10 days after vaccination with IBV 793B virulent strain
- 21 days after vaccination with IBV M41
- 56 days after vaccination with IBVM41 and IBV 793B virulent strain
Protection was assessed by determination of ciliary activity five days after challenge. To confirm the up take and replication of both vaccine strains, in the second study or opharyngeal and cloacal swabs were taken 5 days after vaccination and analysed by PCR.
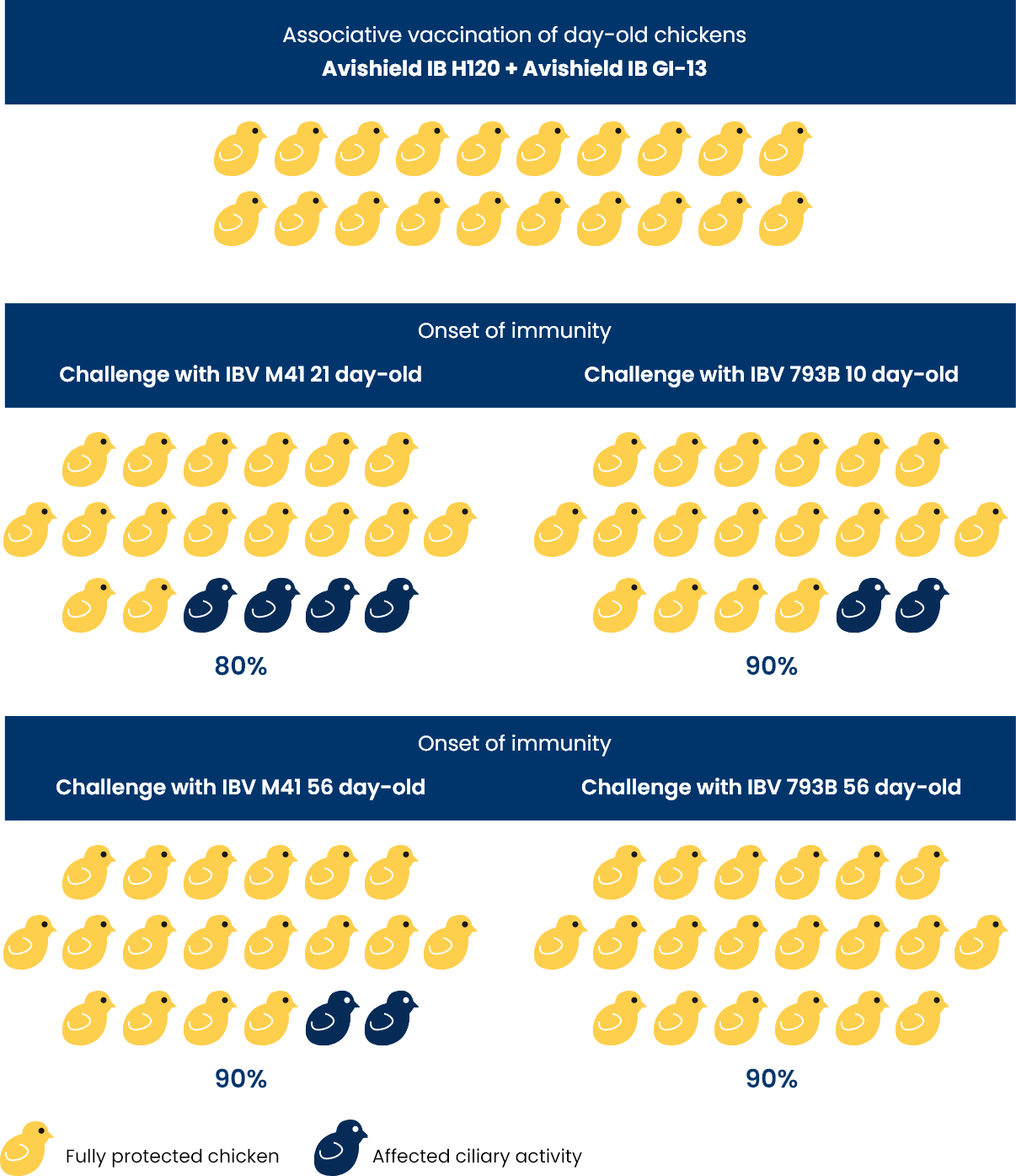
Achieved protection (%) against virulent IBV M41 and 793B strains after associative use of vaccines
Results
- No clinical abnormalities or mortality attributable to the IBV vaccine viruses occurred.
- The associative use of IBV vaccine strains H120 and V-173/11 yielded 90% protection 10 days and 100 protection 56 days after vaccination against challenge with virulent IBV 793B.
- Against challenge with virulent IBV M41 it has yielded 80% protection 21 days and 90% 56 days after vaccination.
- PCR results confirmed presence of IBV virus RNA in all swab samples, with V-173/11 detected in 93% of oropharyngeal and 60% of cloacal swabs, and H120 in 40% of oropharyngeal and 7% of cloacal swabs.
| Vaccine strain | Oropharingeal swab | Oropharingeal swab | ||
| positive / total samples | % of positive samples | Positive / total samples | % of positive samples | |
| IBV V-173/11 | 14/15 | 93% | 9/15 | 60% |
| IBV H120 | 6/15 | 40% | 1/15 | 7% |
Conclusion
Associative use of IBV vaccine strains V-173/11 and H120 administered by spray in minimal doses on the day of hatch results in high vaccine uptake and level of protection against challenge with virulent IBV M41 and IBV 793B strains.
