Fish provide a superb high quality protien source
Rich in preformed DHA and EPA omega-3 fatty acids
Balanced amino acid profile
Easily digestible
Low in saturated fat
Rich in essential vitamins and trace elements including: vitamins D and B2 (riboflavin), calcium, phosphorus, iron, zinc, iodine, magnesium and potassium
The health benefits of omega-3
BRAIN AND EYE DEVELOPMENT
DHA omega-3 fatty acids are the main building blocks of the brain and retina and play an important role in building brain cell membranes and the promotion of new brain cell formation
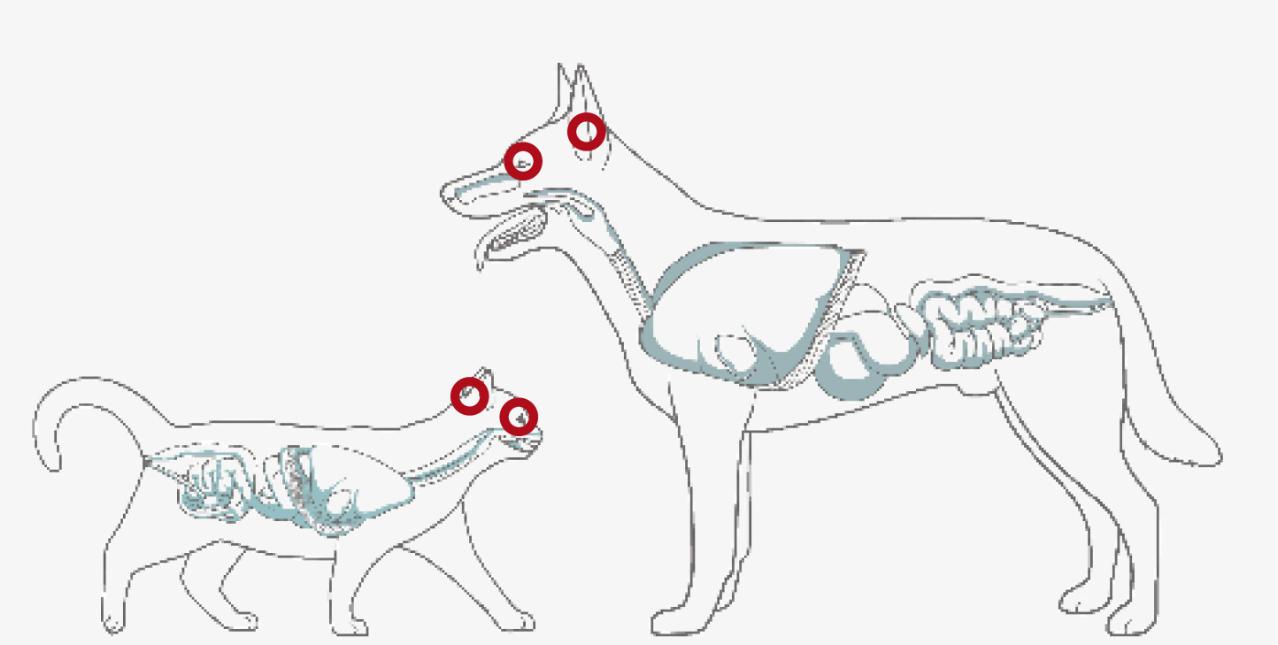
COAT AND SKIN SUPPORT
Omega-3 supports the body’s natural anti-inflammatory process helping to relieve the distressing itching. In addition, fish oils are involved in the production of sebum, an oily waxy substance that lubricates the skin and coats the hair with a protective oily layer to give it a shine.
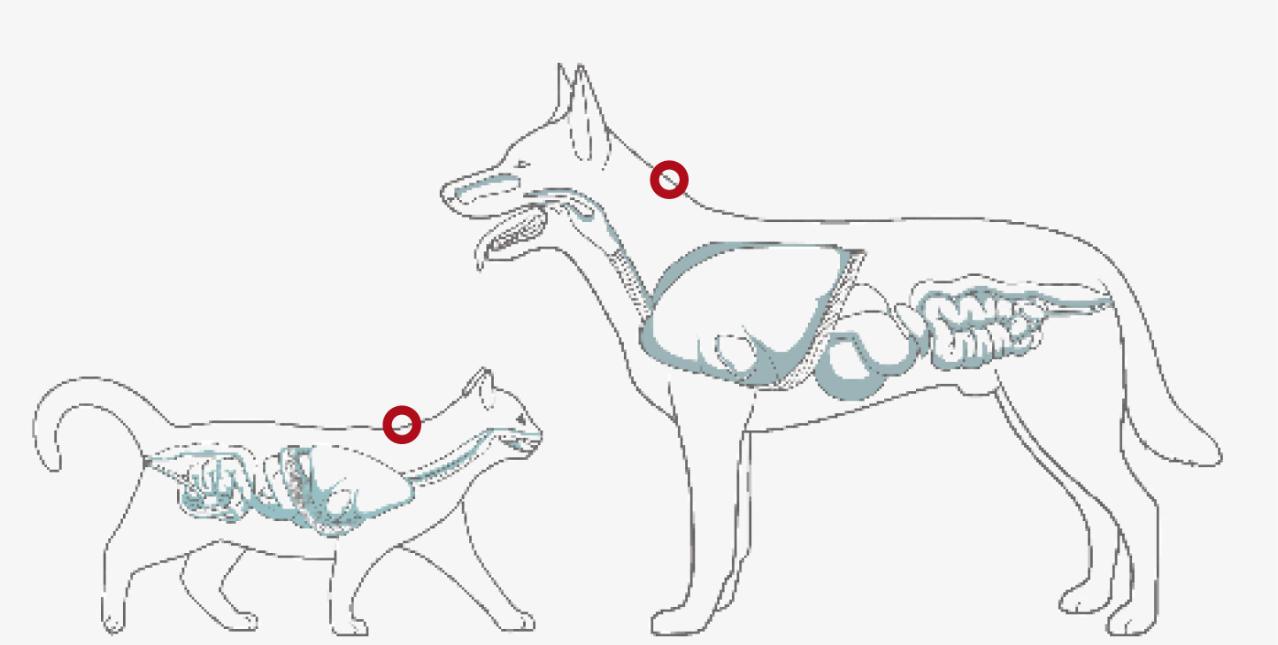
CARDIAC SUPPORT
High level of omega-3 fatty acids can support maintenance of lean body mass, appetite and normal cardiac rhythm
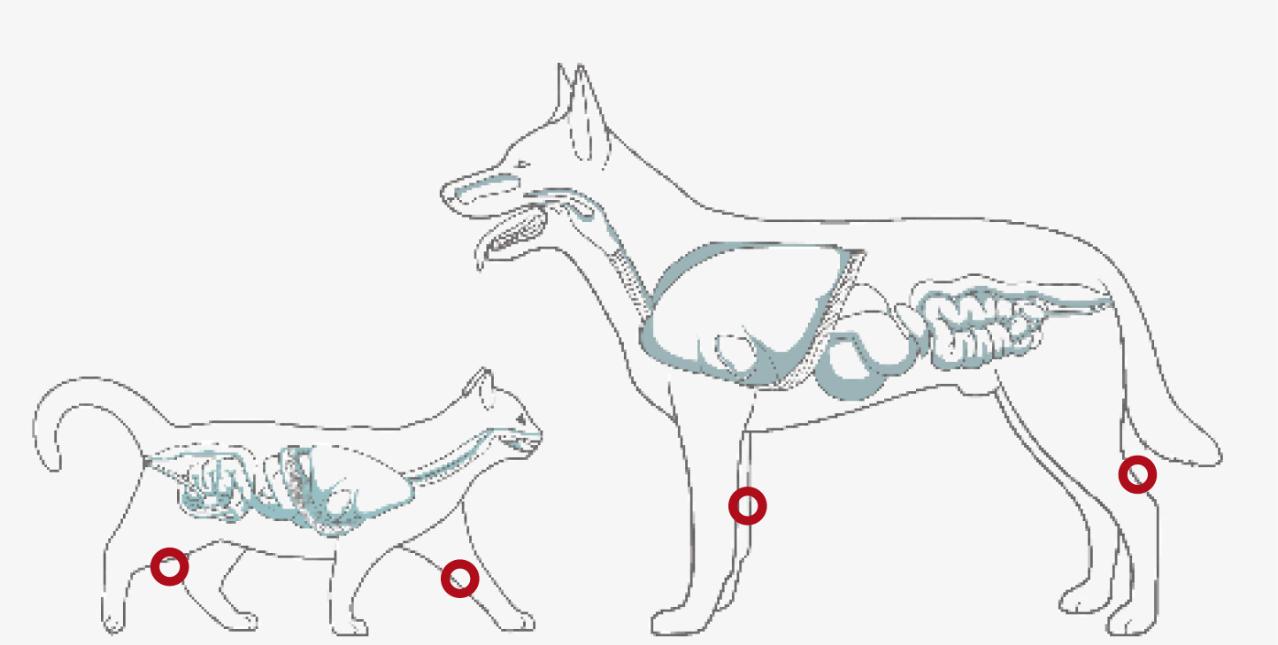
JOINT AND MOBILITY SUPPORT
Omega-3 from fish both helps to reduce the activity of cartilage damaging enzymes and supports the natural anti-inflammatory process to support healthy joints and mobility
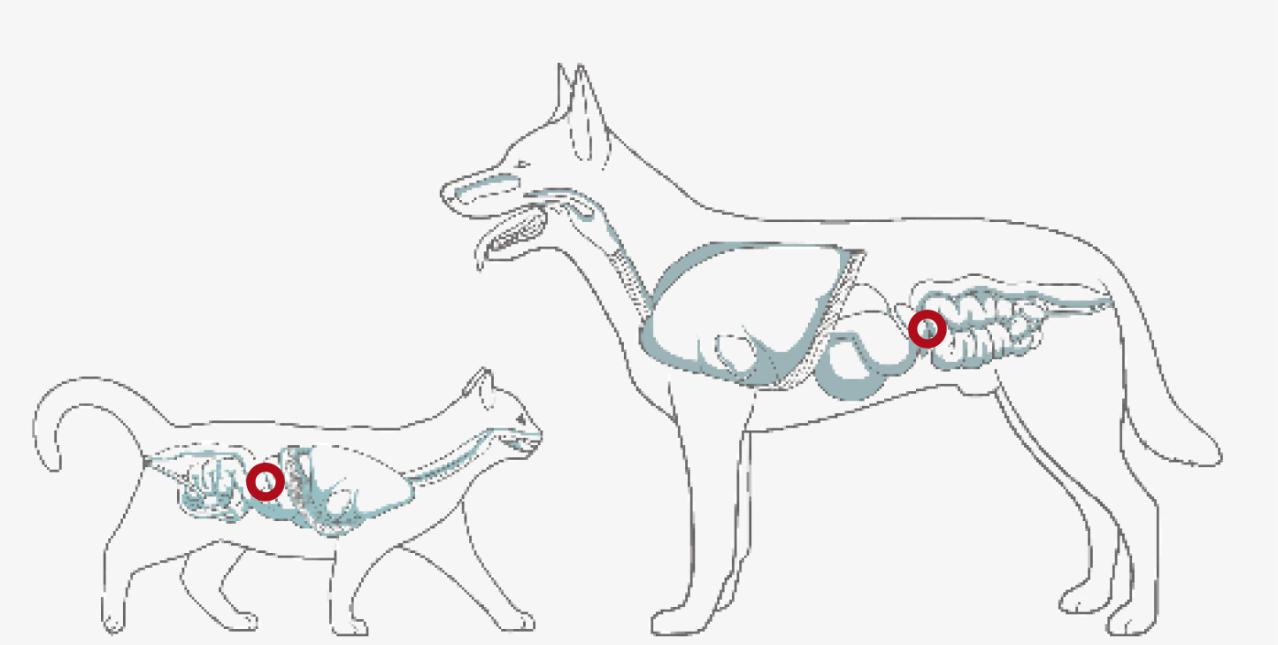
URINARY CRYSTALS
Increased dietary fatty acids can alter serum fatty acid concentrations and lower risk of urine stone formation in cats.
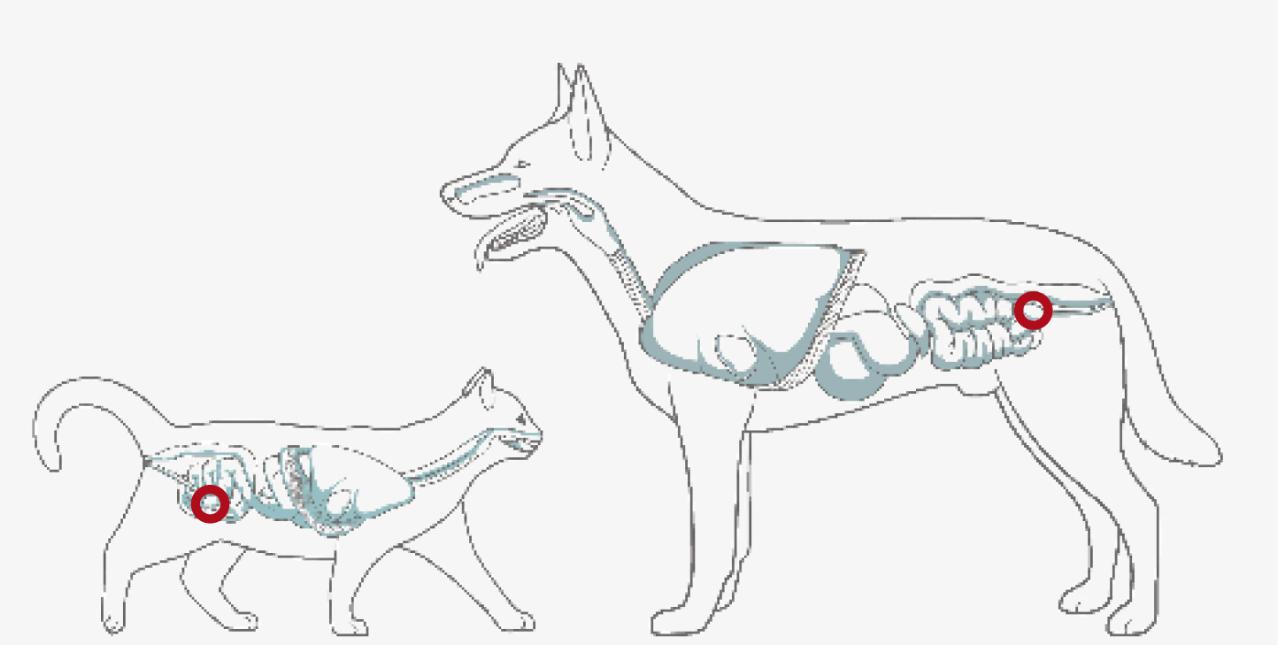
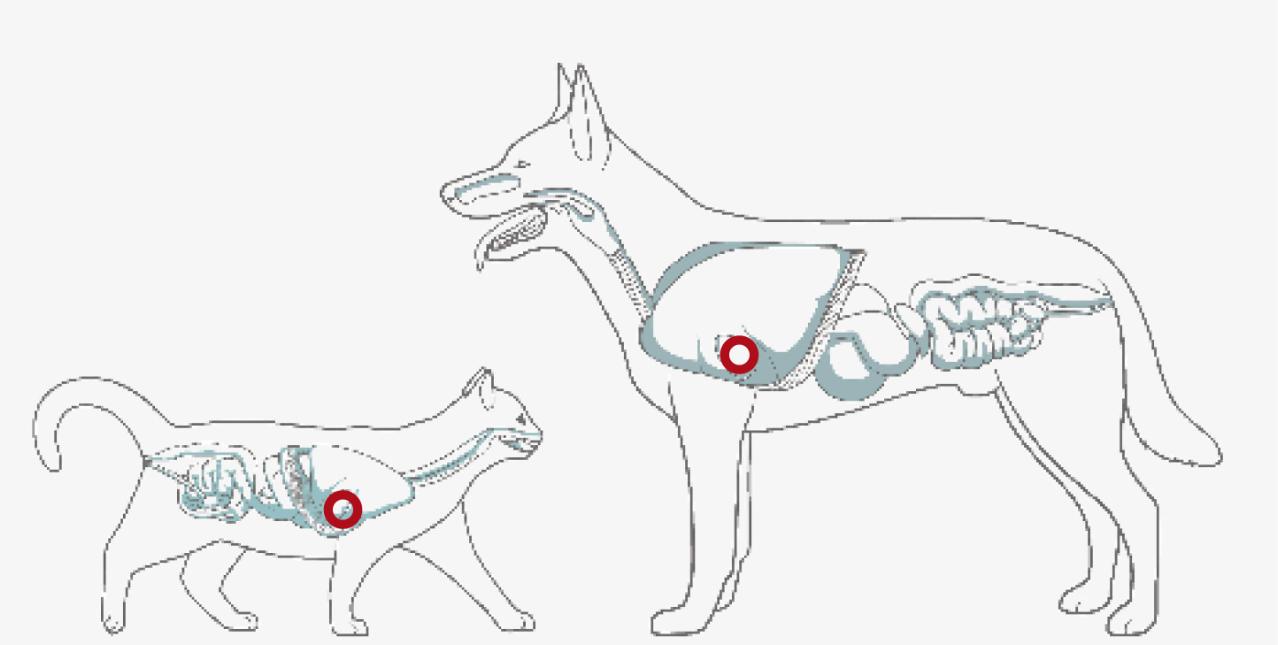
COLITIS
By supporting the body’s natural anti-inflammatory processes omega-3 can help maintain remission in ulcerative colitis – an inflammation of the inner lining of the colon
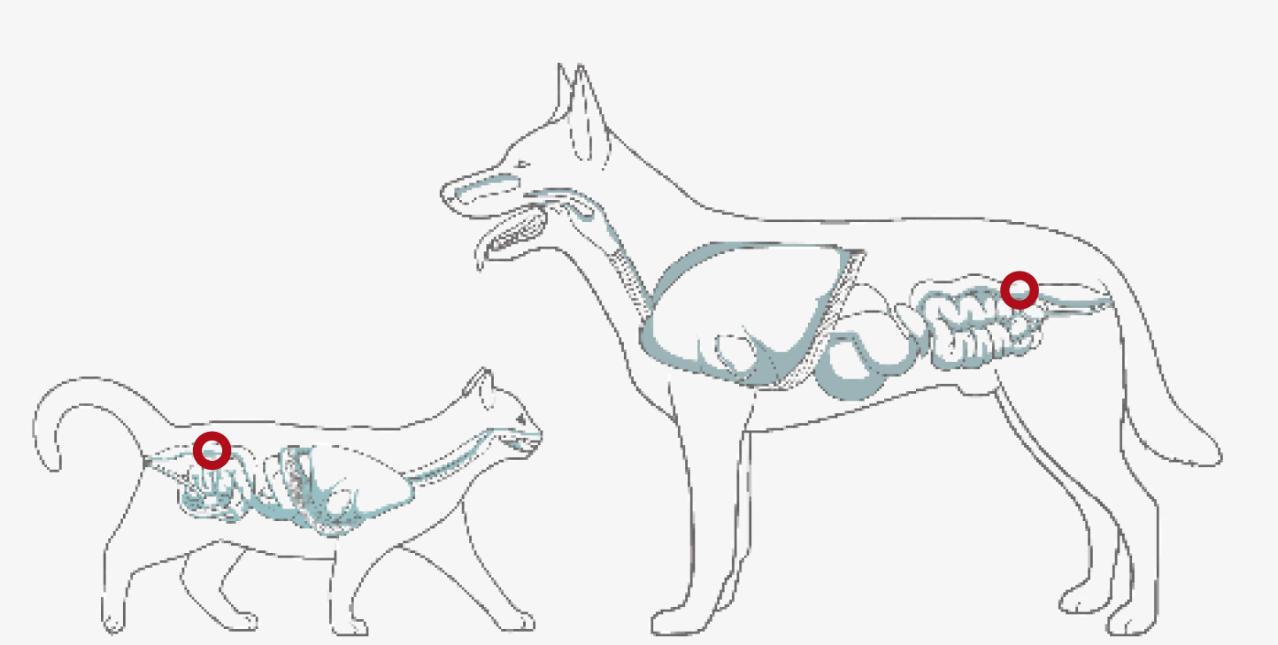
IMMUNE SYSTEM SUPPORT
Recent studies have suggested that omega-3 may have a role in boosting immune b cells activity
Essential fatty acids pathways
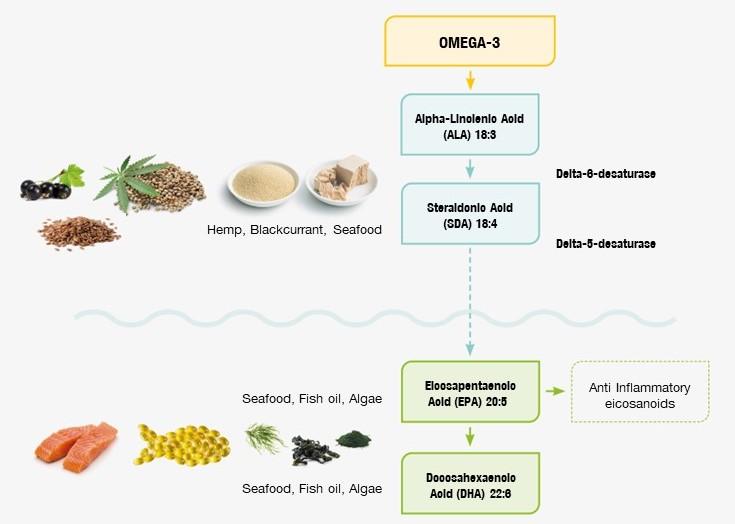
Linoleic acid (LA) is the parent fatty acid of the omega-6 group and alpha linolenic acid (ALA) of the omega-3 group.
Vegetable oils like sunflower oil and safflower oil are a rich source of LA, and ALA is present in linseed or flaxseed oil.
Essential fatty acids needs to be provided through the diet, but once in the body, LA and ALA can be further desaturated and elongated by means of enzymes.
Within the omega-6 family, linoleic acid (LA) can be metabolized into gamma-linolenic acid (GLA), dihomo-gamma-linolenic acid (DGLA) and arachidonic acid (AA).
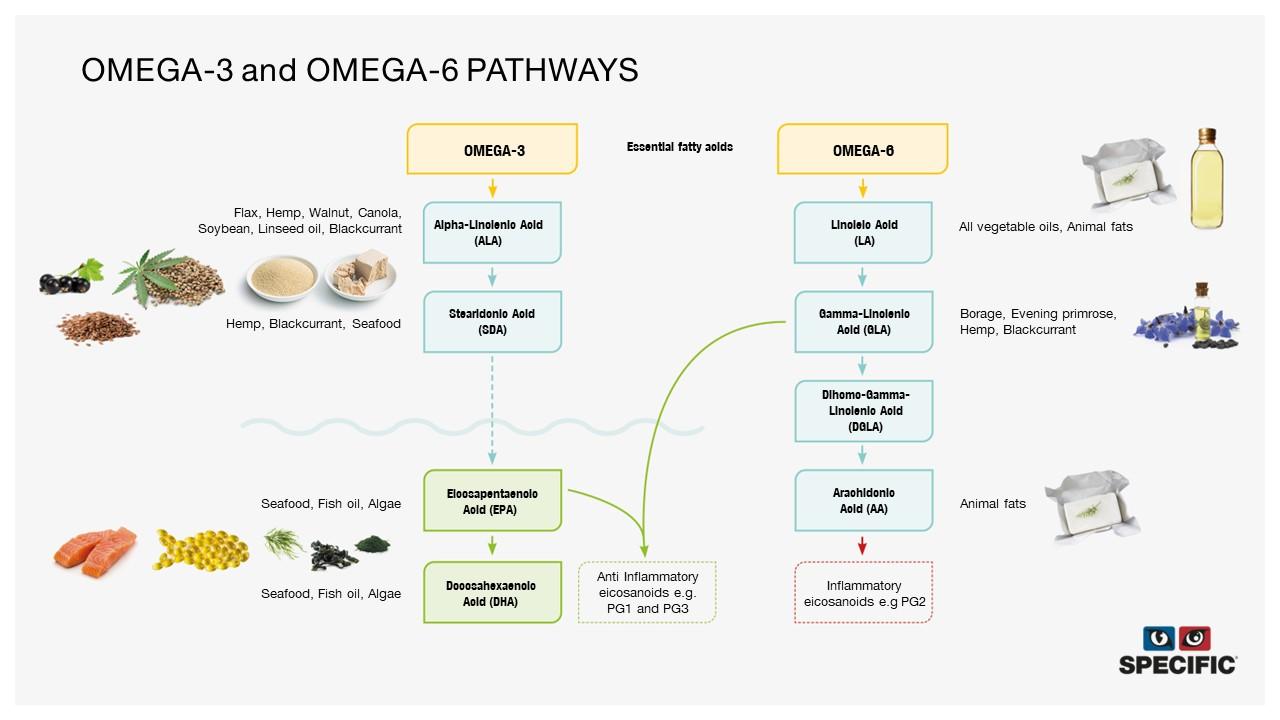
Within the omega-3 family, ALA can be metabolized to form eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). However the activity of the desaturase enzymes is very low in dogs and almost absent in cats, so metabolisation of ALA into EPA and DHA and LA into GLA is very inefficient.
However, EPA and DHA can also be directly taken from dietary intake from marine sources as fish oil, algae and krill. Consumption of borage oil or evening primrose oil provides GLA.
Vegetable derived omega-3s are not effective sources of the beneficial EPA
Omega-3 from vegetable sources is ALA but it is the EPA omega-3 that is metabolised into eicosanoids that supress inflammation
The metabolic conversion of ALA to EPA is very low in dogs and virtually zero in cats due to low activity of the enzyme delta-6 desaturase
Preformed EPA omega-3 from marine sources is preferable
Omega-3 and the inflammatory response
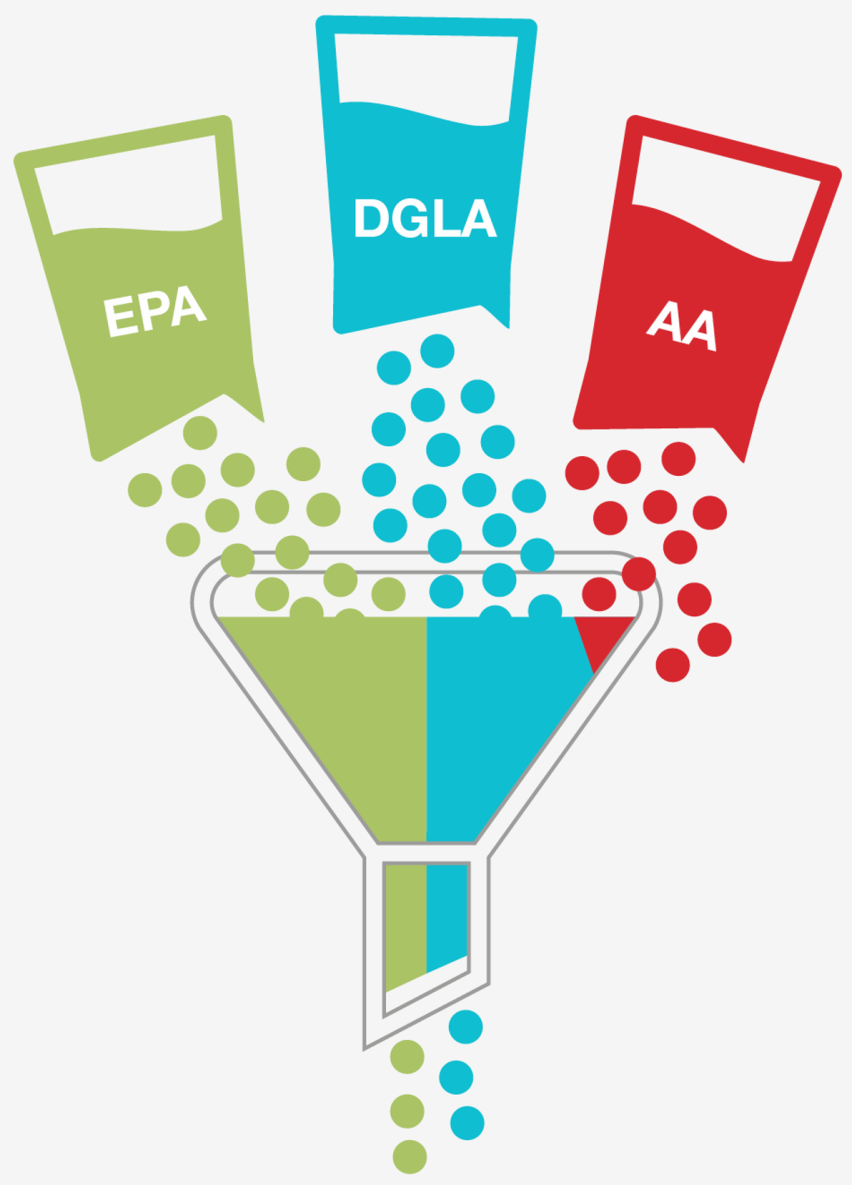
Omega-6 and omega-3 fatty can be metabolised into eicosanoids - locally active, short-living, hormone-like mediators
Eicosanoids from omega-6 fatty acid AA are inflammatory
Eicosanoids from omega-3 fatty acid EPA and omega-6 fatty acid DGLA are not inflammatory
Omega-3 fatty acid EPA and omega-6 fatty acid DGLA compete for the same enzymatic pathways as AA so a strong presence of EPA and DGLA will inhibit inflammation by blocking production of inflammatory eicosanoids
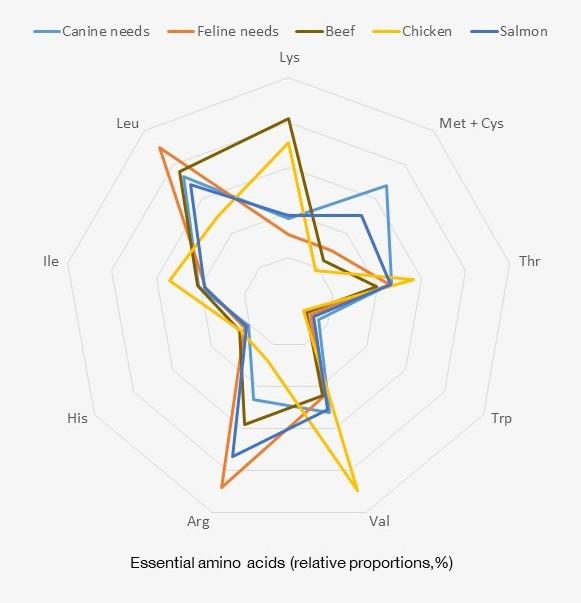
Fish has a well balanced amino acid profile
Fish protein is better balanced, to the amino acid needs of cats and dogs, than beef and chicken
Fish used in SPECIFIC diets
FISH MEAL
A ground powder made from cooked fish providing a concentrated protein source. Meals are highly concentrated sources of essential nutrients, allowing us to add significant levels of nutrients without adding excessive moisture.
Our fish meal is made from different wild caught certified Atlantic white fish.

FISH OIL
Fish oil is a natural product and so will have variable amounts of EPA & DHA Omega-3.
At SPECIFIC we use a specially blended fish oil made from cod liver oil and anchovy oil to ensure consistent and high levels of Omega-3 fatty acids.

FRESH SARDINE
Used in some of our diets is a fresh whole MSC certified sardine caught off the Cornish coast by small boats using ring netting – a catch system that significantly reduces by-catch, fuel usage and seabed damage.

HYDROLYSED SALMON PROTEIN
Made from Norwegian and Scottish farmed salmon.

ALGAE
Aquatic plants and a rich source of omega-3. We use algae in many of our diets
Algae provides a highly sustainable form of high quantities and consistent levels of omega-3 – especially DHA
Algae grow incredibly fast and can be grown on non-productive, non-arable land so use fewer environmental resources
Algae production grew from a NASA programme, looking how to feed mars colonists

